📚 Table of Contents
In today’s hyper-competitive landscape, guesswork is a luxury no organization can afford. What if every critical choice you made was backed by concrete evidence, historical trends, and predictive analytics rather than intuition alone? The transition from instinct-based to information-based leadership is the defining characteristic of modern successful enterprises. This comprehensive guide delves into the essential strategies and practical steps to embed data-driven decision-making into the very DNA of your organization, ensuring that every move you make is informed, strategic, and primed for success.
Laying the Foundation for Data-Driven Success
The journey toward data-driven decision-making begins with a solid foundation. This involves more than just purchasing software; it requires a fundamental shift in how data is perceived, collected, and managed. The first step is to ensure data quality. Inaccurate, incomplete, or inconsistent data is worse than no data at all, as it leads to misguided conclusions and costly mistakes. Implementing rigorous data governance policies is non-negotiable. This means establishing clear ownership of data assets, defining standards for data entry and maintenance, and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations like GDPR or CCPA. For example, a retail company must standardize how product categories are entered across all point-of-sale systems to accurately analyze sales performance. Without this clean, reliable data, any subsequent analysis is built on a shaky foundation.
Next, organizations must focus on data accessibility. Data silos, where information is trapped within specific departments like marketing or finance, are a major impediment to holistic analysis. Breaking down these silos through integrated platforms like a cloud data warehouse allows for a 360-degree view of the business. A customer’s journey, from first seeing an ad to making a purchase and then seeking support, can be tracked and analyzed seamlessly. This integrated view is crucial for understanding complex interactions and drivers of behavior. Furthermore, accessibility means providing user-friendly tools for non-technical staff. When a marketing manager can easily run a report to see the ROI of a recent campaign without waiting weeks for the IT department, the organization moves much faster and more efficiently.
Cultivating a Data-Driven Culture
A technological infrastructure is useless without a culture that embraces it. Cultivating a data-driven culture starts at the top. Leadership must not only endorse but actively champion the use of data in every meeting and strategic discussion. When leaders consistently ask, “What does the data say?” they send a powerful message that opinions must be supported by evidence. This cultural shift also requires extensive training and upskilling. Employees at all levels need to become data-literate; they must understand basic data concepts, know how to interpret key metrics relevant to their role, and feel comfortable questioning assumptions based on what the numbers reveal.
Celebrating successes rooted in data analysis is a powerful motivator. If a sales team uses data to identify an untapped market segment and achieves record sales, that victory should be highlighted company-wide as a testament to the data-driven approach. Conversely, it’s vital to create a safe environment where data-driven failures are treated as learning opportunities rather than reasons for blame. If an analysis leads to a failed product launch, the focus should be on interrogating the data model, the assumptions made, and the interpretation of the results to learn for next time. This fosters a culture of experimentation and continuous improvement, where data is a guide for exploration rather than a rigid answer key.
Mastering the Data Analysis Process
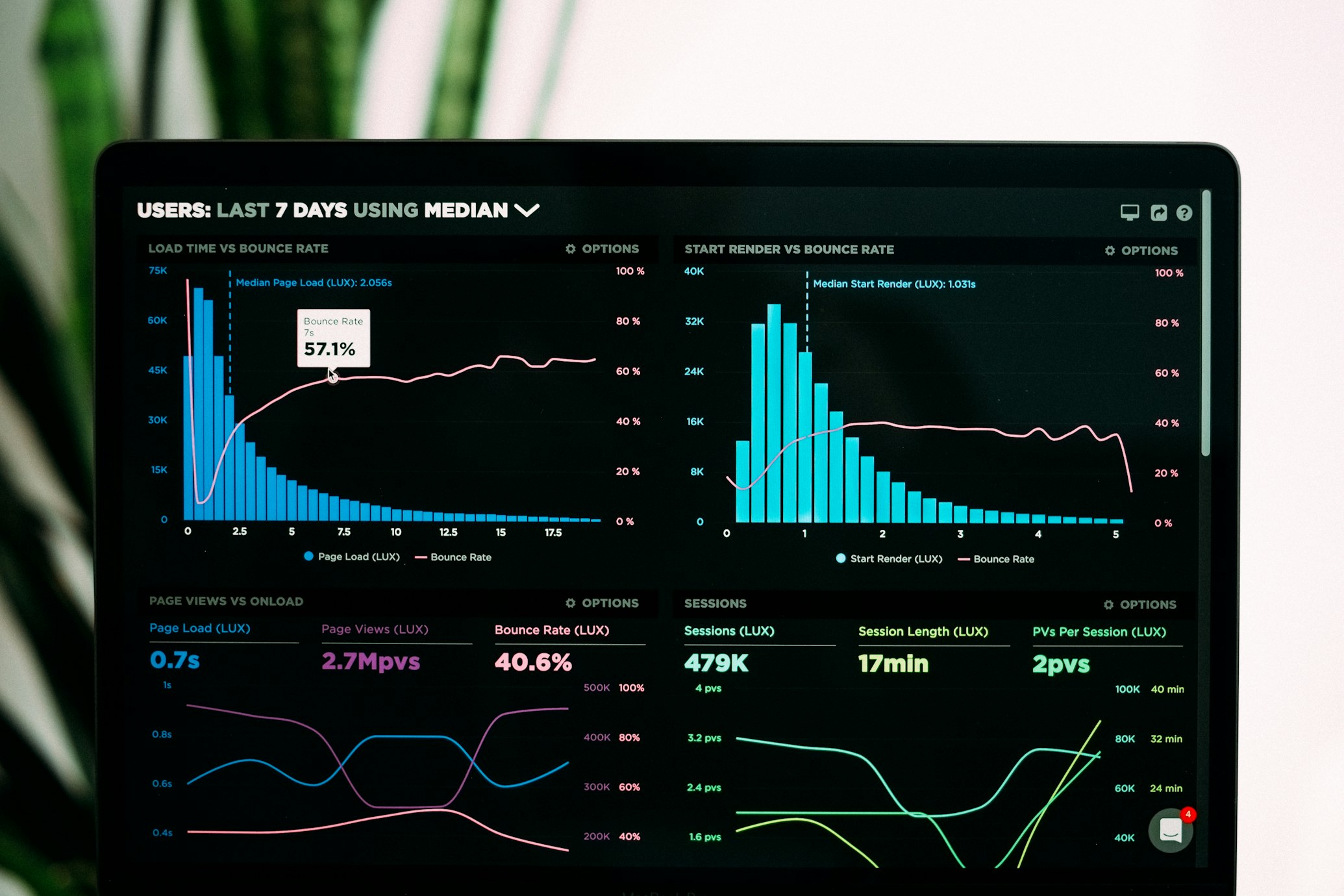
Effective data-driven decision-making relies on a disciplined analytical process. It begins with asking the right business questions. A vague question like “how can we improve sales?” is less effective than a targeted one like “which marketing channel has the highest customer acquisition cost for users aged 25-34?” This specificity guides the entire analysis. Once the question is defined, the next step is data collection and preparation, which often consumes the majority of an analyst’s time. This involves gathering data from various sources, cleaning it, handling missing values, and transforming it into a usable format.
The core of the process is the application of appropriate analytical techniques. This ranges from descriptive analytics (What happened?) using dashboards and reports to diagnostic analytics (Why did it happen?) using drill-downs and correlation analysis. More advanced organizations employ predictive analytics (What will happen?) using statistical models and machine learning to forecast trends, and prescriptive analytics (What should we do?) which suggests actionable recommendations. For instance, a logistics company might use predictive analytics to forecast shipping demand and prescriptive analytics to optimize delivery routes in real-time, saving millions in fuel and time costs. The key is to match the analytical method to the complexity of the business question at hand.
Leveraging the Right Tools and Technologies
The modern data stack provides an arsenal of tools that empower organizations of all sizes. For data storage and management, cloud data warehouses like Snowflake, Google BigQuery, and Amazon Redshift offer scalable, powerful solutions that eliminate traditional infrastructure constraints. Data integration and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tools such as Stitch, Fivetran, or Talend automate the process of moving data from source systems into the warehouse, ensuring data is always fresh and available for analysis.
On the analytics front, business intelligence (BI) platforms like Tableau, Power BI, and Looker are indispensable. They allow users to create interactive visualizations and dashboards that make complex data understandable at a glance. For more advanced work, data science platforms like DataRobot or programming languages like Python and R provide the environment for building sophisticated machine learning models. The critical factor is choosing tools that are appropriate for your team’s skill level and your organization’s specific needs. A small startup might begin with a simple BI tool connected to a few key data sources, while a large enterprise may require a full suite of integrated platforms to manage its entire data ecosystem.
Turning Insights into Decisive Action
The entire value of data analysis is realized only when insights are translated into action. This requires clear communication. A data scientist might discover a complex pattern, but if they cannot explain it in simple terms to the decision-makers, the insight is wasted. Data storytelling is therefore an essential skill. This involves crafting a narrative around the data, using visualizations to highlight key findings, and clearly outlining the implications and recommended actions. A good dashboard doesn’t just show numbers; it tells a story about what those numbers mean for the business.
Finally, establishing a feedback loop is crucial for continuous improvement in data-driven decision-making. After implementing a decision based on data, you must measure its outcomes. Did the new marketing campaign achieve the projected lift in conversions? Did the inventory optimization model reduce carrying costs as predicted? By systematically tracking the results of data-driven actions, you validate your analytical models, refine your processes, and build an ever-growing repository of institutional knowledge about what works and what doesn’t. This creates a virtuous cycle where each decision informs the next, leading to progressively smarter and more effective business strategies.
Conclusion
Becoming a truly data-driven organization is not a destination but a continuous journey of refinement and learning. It demands a commitment to quality data, a cultural embrace of evidence-based thinking, mastery of analytical processes, strategic use of technology, and, most importantly, the courage to act on the insights discovered. By methodically implementing these strategies, you move beyond simply having data to truly being driven by it, unlocking new levels of efficiency, innovation, and competitive advantage that define market leaders.

Leave a Reply